CUDA Stencil Benchmark
High-performance CUDA kernel generation and benchmarking framework
View the Project on GitHub jasonlarkin/cuda-stencil-benchmark
LLM-Guided Kernel Generation Workflow
Overview
This document describes the iterative workflow for generating and optimizing CUDA kernels using language models. The workflow emphasizes correctness-first validation and systematic performance optimization.
Workflow Diagram
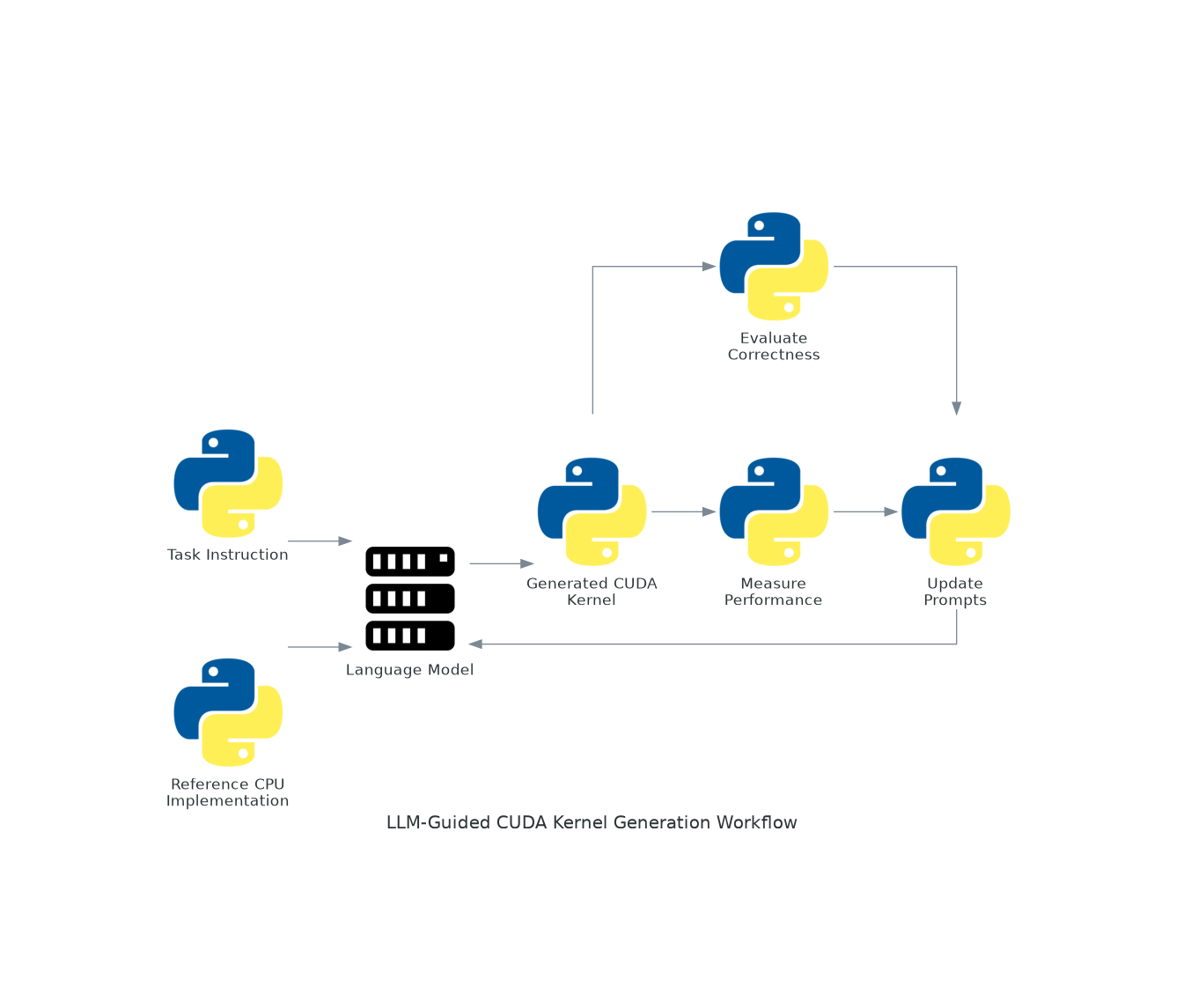
Workflow Phases
1. Specification
Inputs:
- Task specification (
tasks/<task>/spec.md) - Problem shapes (
tasks/<task>/shapes.yaml) - Interface definition (
include/iface.h)
Output: Complete task definition with correctness criteria and performance targets.
2. Prompt Construction
Components:
- System Constraints (
prompts/system.md): Correctness priority, optimization guidelines - Task Template (
prompts/task_template.md): Task-specific instructions, interface requirements - Few-Shot Examples (
prompts/few_shots.md): Reference kernel patterns, optimization techniques
Output: Complete prompt for language model.
3. Kernel Generation
Process:
- Send prompt to language model
- Receive generated CUDA kernel code
- Save to
cuda/kernels/XXX_name/kernel.cu
Output: CUDA kernel source file.
4. Compilation Test
Process:
cd cuda
make ATTEMPT=XXX_name ARCH=sm_75
Outcomes:
- Success: Proceed to correctness test
- Failure: Document error, update prompt, regenerate
5. Correctness Test
Process:
VERIFY=1 ./bench_cuda_XXX_name
Method:
- Run CPU reference kernel
- Run CUDA kernel
- Compare checksums and per-voxel differences
Criteria:
- Checksum difference < tolerance (1e-5)
- Max per-voxel difference < tolerance
Outcomes:
- Pass: Proceed to performance benchmark
- Fail: Document discrepancy, update prompt, regenerate
6. Performance Benchmark
Process:
CSV=1 ./bench_cuda_XXX_name > results.csv
./dev_bw # Measure device bandwidth
Metrics:
- Execution time (update + sources)
- Throughput (points/second)
- GF/s achieved
- Device bandwidth
7. Performance Analysis
Roofline Analysis:
- Calculate arithmetic intensity (AI = FLOPs / Bytes)
- Measure device bandwidth
- Compute roofline ceiling
- Plot measured performance vs roofline
Interpretation:
- Memory-Bound: Performance limited by bandwidth → optimize memory access patterns
- Compute-Bound: Performance limited by compute → optimize instruction efficiency
8. Feedback Loop
Analysis:
- Compare performance vs baseline
- Identify bottlenecks (memory vs compute)
- Document optimization insights
Prompt Updates:
- Add successful optimization patterns
- Document failure modes to avoid
- Update few-shot examples
- Refine task instructions
Next Iteration: Generate new kernel variant or refine existing kernel.
Example: Iterative Kernel Development
Initial Generation
- Prompt: “Generate tiled kernel with x-y shared memory”
- Result: Kernel with shared memory tiling
Compilation
- Status: Success
Correctness Test
- Status: FAIL
- Issue: Source injection parity broken
- Fix: Update prompt to emphasize source injection semantics
Regeneration
- Updated Prompt: Includes source injection requirements
- Result: Corrected kernel
Correctness Test (Retry)
- Status: PASS
- Checksum: Within tolerance
Performance Benchmark
- Result: Slower than baseline
- Analysis: Broken memory coalescing
- Insight: Tiling x-y planes degrades z-coalescing
Feedback
- Documentation: Tiling strategy ineffective for this memory layout
- Prompt Update: Emphasize z-coalescing for this data layout
- Next Kernel: Focus on z-coalescing optimizations
Implementation Status
Implemented Components
Phase 1: Specification - COMPLETE
- Task specifications (
tasks/fctd3d/,tasks/matmul/) - Interface definitions (
include/iface.h) - Problem shapes and configurations
Phase 2: Prompt Construction - COMPLETE
- System constraints (
prompts/system.md) - Task templates (
prompts/task_template.md) - Few-shot examples (
prompts/few_shots.md)
Phase 5: Correctness Test - COMPLETE
- CPU reference benchmark (
cpu_bench/bench_main.cpp) - Test framework with pytest (
tests/) - Result tracking system (
tests/test_tracker.py)
Phase 6: Performance Benchmark - COMPLETE
- CPU benchmarking infrastructure
- Performance sweep scripts
- CSV output format
Phase 7: Performance Analysis - COMPLETE
- Roofline bandwidth measurement (
roofline/stream_triad) - Roofline plotting (
roofline/plot_roofline.py) - Analysis tools (
analysis/compare_cpu_gpu.py)
Manual Components
Phase 3: Kernel Generation - MANUAL
- LLM generation happens externally
- Developer manually places kernel in
cuda/kernels/XXX_name/kernel.cu - No automated LLM API integration
Phase 4: Compilation Test - MANUAL
- Developer runs
make ATTEMPT=XXX_name - Compilation errors handled manually
- No automated error feedback to LLM
Phase 8: Feedback Loop - MANUAL
- Developer analyzes test results
- Developer manually updates prompts
- No automated prompt modification
Pending Components
CUDA Infrastructure - PENDING
- CUDA harness and build system
- CUDA kernel attempts
- Device bandwidth measurement
- Colab automation scripts
Key Principles
- Correctness-First: Verify numerical parity before performance optimization
- Systematic Testing: Automated correctness and performance validation
- Iterative Improvement: Use test results to inform prompt updates (manual)
- Performance Characterization: Roofline analysis guides optimization strategy
Success Metrics
- Correctness: All kernels pass correctness tests with numerical parity maintained
- Performance: Significant speedup over CPU (target: 5-10×) with near roofline performance
- Workflow: Systematic testing infrastructure, reproducible results, clear documentation